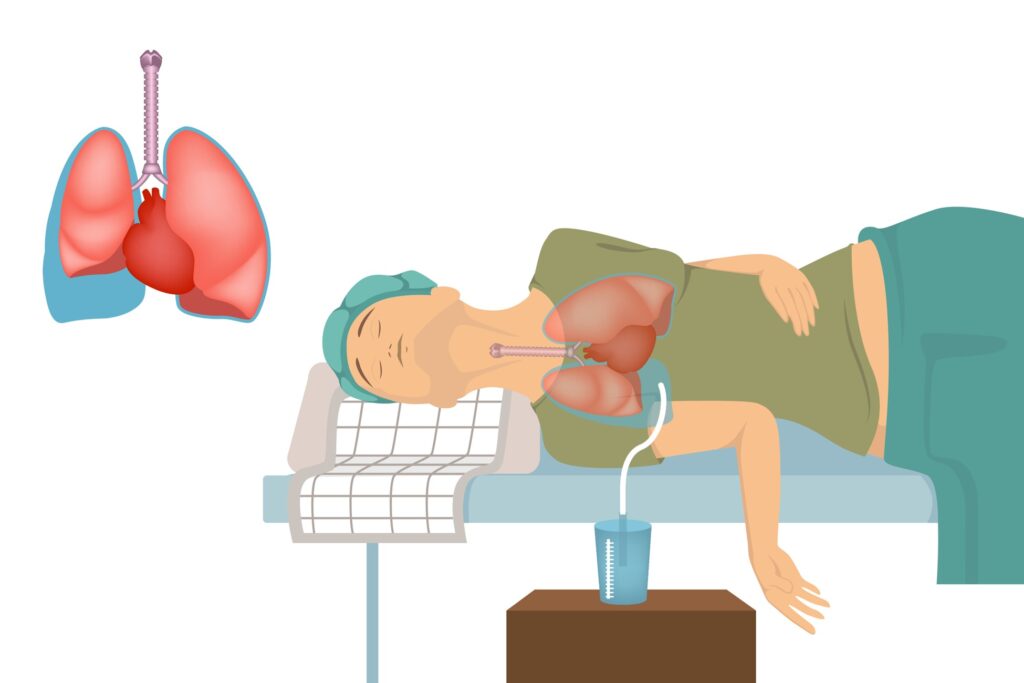
Pleural effusion is a condition in which fluid builds up in the space between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest wall.
This fluid can cause shortness of breath and chest pain. It can also put pressure on the lungs and heart, making it difficult to breathe.
This can occur due to a variety of causes, including infection, heart failure, and cancer.
Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dry cough
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing while lying down
- Rapid heart rate
- Unexplained weight loss
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Wheezing
Diagnosis of Pleural effusion
The diagnosis of pleural effusion usually begins with a physical exam. The doctor will listen for abnormal sounds from the lungs with a stethoscope.
If a pleural effusion is suspected, the doctor may order imaging tests such as an X-ray or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis.
In some cases, other tests may be ordered, such as a chest ultrasound or a thoracentesis, which is a procedure to remove fluid from the pleural space for analysis.
Treatment of Pleural effusion
Treatment for pleural effusion usually depends on the underlying cause, but may include:
- Medications to treat the underlying condition, such as antibiotics for infection or steroids for inflammation
- Drainage of excess fluid from the pleural space (thoracentesis)
- Surgery to repair a damaged pleural space, such as a pleurodesis
- Radiation therapy for cancerous effusions
- Chemotherapy for cancerous effusions
Tips to Help Deal with Pleural Effusion
1. Take prescribed medications as directed: Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking any medications prescribed for pleural effusion, such as antibiotics or diuretics.
2. Get plenty of rest: Make sure to rest and relax as much as possible. This will help your body recover and reduce any pain or discomfort.
3. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help thin the fluid in the pleural space and reduce the pressure on the lungs.
4. Exercise: Gentle exercise can help improve breathing and reduce the risk of complications.
5. Eat a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and proteins can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
6. Avoid smoking: Smoking can worsen the symptoms of pleural effusion and should be avoided.
7. Monitor your symptoms: Pay attention to any changes in your breathing or other symptoms and contact your doctor if they worsen.
Myth and Fact on Pleural Effusion
Myth: Pleural effusion always indicates lung cancer.
Fact: While it can be a sign of lung cancer, it can also be caused by a variety of other conditions, including infections, heart failure, pulmonary embolism, and inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.